SWOT ANALYSIS: A THEORETICAL REVIEW
SY BCA
Assignment -2
1. INTRODUCTION :
Today most organizations engage in strategic planning. Strategic planning is a way to help an organization be more productive by helping guide the allocation of resources in order to achieve goals. It is a strategic management tool. In other words it is a part of strategic management. In fact, strategic planning is a key to successful strategic management.
Strategic management is the continuous process of creating, implementing and evaluating decisions that enable an organization to achieve its objectives. Strategic management allows an organization to be more proactive than reactive in shaping its own future; it allows an organization to initiate and influence - rather than just respond to- activities -and thus to exert control over its own destiny (David, 2003: 15). Strategic management consists of the analysis, decisions, and actions an organization undertakes in order to create and sustain competitive advantages. The strategic management process is a sequential set of analyses and choices that can increase the likelihood that an organization will choose ‘good strategy’, that is, that generates competitive advantages. It begins with vision. Vision is a picture of the future. It describes the desired future position of the organization. The second step of strategic management process is mission. An organization’s mission is its long-term purpose. Missions define both what an organization aspires to be in the long run and what it wants to avoid in the meantime. Objectives are the third step of strategic management process. Objectives are concrete goals that an organization seeks to reach. The next phases of the strategic management process is external and internal analysis, also called SWOT Analysis. By conducting an external analysis, an organization identifies the critical threats and opportunities in its competitive environment.
1: The Strategic Management Process 2.
SWOT Analysis is a tool used for strategic planning and strategic management in organizations. It
can be used effectively to build organizational strategy and competitive strategy. In accordance with the
System Approach, organizations are wholes that are in interaction with their environments and consist of
various sub-systems. In this sense, an organization exists in two environments, one being in itself and the
other being outside. It is a necessity to analyse these environments for strategic management practices. This
process of examining the organization and its environment is termed SWOT Analysis.
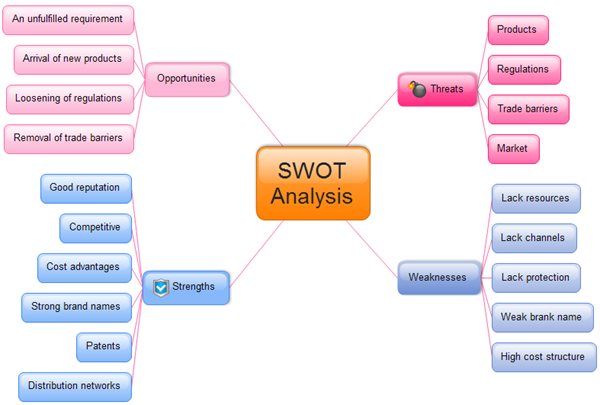
“SWOT Analysis is a simple but powerful tool for sizing up an organization’s resource capabilities and deficiencies, its market opportunities, and the external threats to its future” (Thompson et al., 2007: 97). The acronym* SWOT stands for ‘strengths’, ‘weakness’, ‘opportunities’ and ‘threats’. The SWOT Analysis, also referred to as ‘SWOT Matrix’, can also be formulated as ‘TOWS Analysis’ or ‘TOWS Matrix’. As in Turkish, considering the adaptation of the capital letters, the acronym can be indicated as ‘GZFT Analysis/Matrix’ or ‘FÜTZ Analysis/Matrix’. SWOT Analysis is a strategic planning framework used in evaluation of an organization, a plan, a project or a business activity. SWOT Analysis is therefore a significant tool for situation analysis that helps the managers to identify organizational and environmental factors. SWOT Analysis has two dimensions: Internal and external. Internal dimension includes organizational factors, also strengths and weaknesses, external dimension includes environmental factors, also opportunities and threats.
3. THE COMPONENTS OF SWOT ANALYSIS
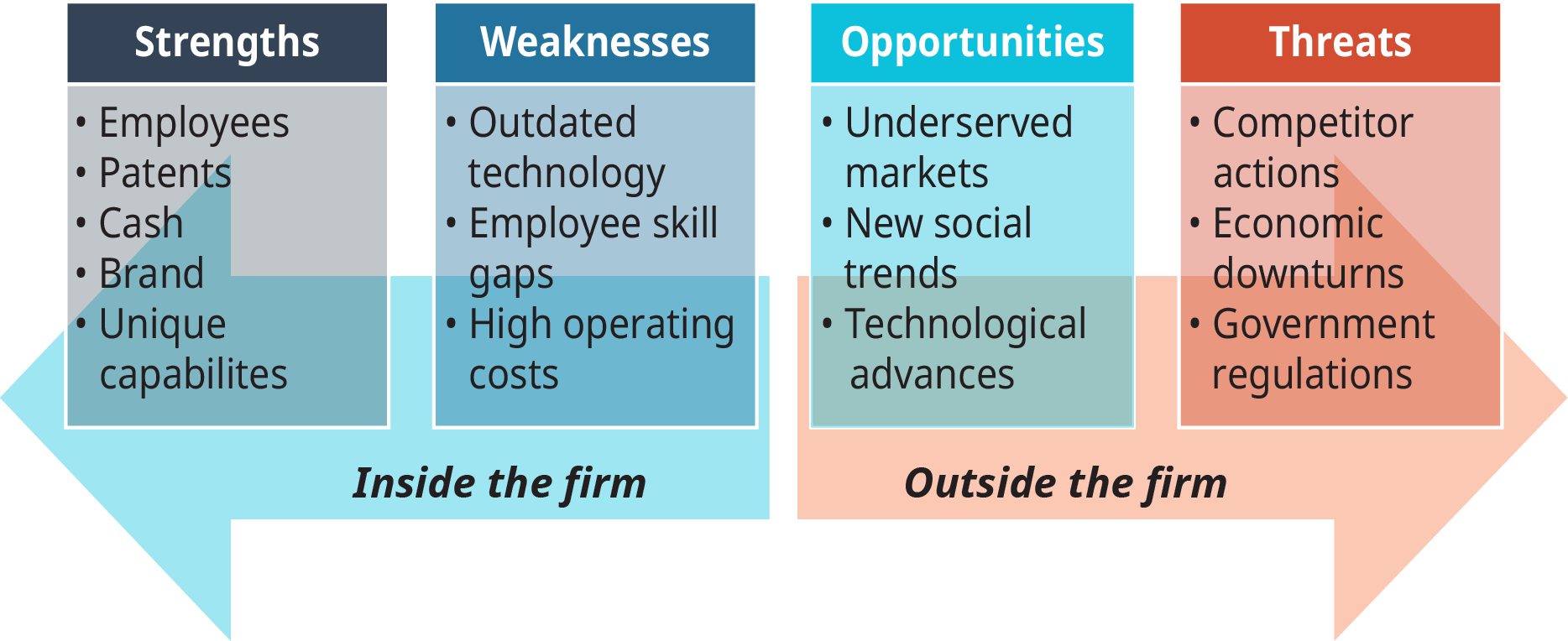
SWOT Analysis is a process that involves four areas into two dimensions. It has four components: ‘Strengths’, ‘weaknesses’, ‘opportunities’, ‘threats’. Strengths and weaknesses are internal factors and attributes of the organization, opportunities and threats are external factors and attributes of the environment. SWOT Analysis is typically drawn out in a four-quadrant box that allows for a summary that is organized according to the four elements in a 2x2 matrix.
In SWOT Analysis, strong and weak aspects of an organization are identified by examining the elements in its environment while environmental opportunities and threats are determined by examining the elements outside its environment. In this sense SWOT Analysis is a strategic planning tool used to evaluate the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats of an organization. It provides information that is helpful in matching the organization’s resources and capabilities to the competitive environment in which it operates. Strengths and opportunities are helpful to achieve the organizational objectives. They are favourable for organizations. Weaknesses and threats are harmful to achieving the organizational objectives. They are unfavourable for organizations. Therefore, underlying any successful selection of strategies is an analysis of the organization’s internal strengths and weaknesses that are posed by internal environment and the opportunities and threats that are posed by the external environment. In other words, manager’s role is to try to ‘fit’ the analysis of externalities and internalities, to balance the organization’s strengths and weaknesses in the light of environmental opportunities and threats. The framework presented in Table 2. identifies many of the variables that management should analyse.
For the organization, it is as important to know its weaknesses as its strengths. The reason is that no strategy can be built upon weaknesses. The organizational weaknesses that have the potential to lead the organization to inefficiency and ineffectiveness should be known and improved. Solving the existing problems that would cause difficulties and limitations for long-term plans and strategies, and foreseeing potential problems are obligatory.
Environmental Opportunities: Opportunity means a situation or condition suitable for an activity. Opportunity is an advantage and the driving force for an activity to take place. For this reason, it has a positive and favourable characteristic. For organizational managements, an opportunity is the convenient time or situation that the environment presents to the organization to achieve its goals. Opportunities are those that would yield positive results for the organization determined as a result of the analysis of its environment. Competition and the intense work presents organizations big opportunities. In fact “opportunities are conditions in the external environment that allow an organization to take advantage of organizational strengths, overcome organizational weaknesses or neutralize environmental threats” (Harrison and St. John, 2004: 164).
(1) how the organization’s strategy can be matched to both its resource capabilities and its market opportunities, and
(2) how urgent it is for the organization to correct which particular resource weaknesses and guard against which particular external threats” (Thompson and Strickland, 2001: 127). Here is an example of a SWOT Analysis for Nike, Inc., which is an American multinational corporation that is engaged in the design, development, manufacturing and worldwide marketing and selling of footwear, apparel, equipment, accessories and services. It is one of the world’s largest suppliers of athletic shoes and apparel and a major manufacturer of sports equipment and most valuable brand among sports businesses. The company was founded in 1962 by Bill Bowerman and Philip H. Knight as a partnership under the name, Blue Ribbon Sports. The company takes its name from Nike, the Greek goddess of victory. Since Germany conquered the domestic market in America, Nike came with low-cost and high quality products for the American people. Today, Nike Inc. is the world’s leading innovator in athletic footwear, apparel, equipment and accessories (http://www.nikeinc.com, 2016).
SWOT Analysis is more than an exercise in making four lists. The really valuable part of SWOT Analysis is determining what story the four lists tell about the organizations’s situation and thinking about what actions are needed. In summary the basic assumption of a SWOT Analysis is that an organization must align internal activities with external realities to be successful. The SWOT Analysis provides a framework for analysing strengths and weaknesses -internal- and opportunities and threats -external-. It helps to focus on minimising weaknesses and taking the greatest possible advantage of opportunities available. As a result, considering external and internal factors is essential because they clarify the world in which the business or the unit operates, enabling it to get a better envision for the desired future (Pahl and Richter, 2009: 4-5).
4. HISTORICAL DEVELOPMENT OF SWOT ANALYSIS
He examined the relationship between what he called institutional leadership and distinctive competence. Selznick suggests institutional leaders focus their attention on safeguarding a firm’s distinctive values and identity from internal and external threats. This organizational vision, in combination with organizational structure, helps define a firm’s distinctive competencies (Selznick, 1957). Alfred Chandler, established the design school’s notion of business strategy and its relationship to structure.
Many scholars suggest the need to use additional analysis instead of SWOT or using it in combination with other techniques.
5. ADVANTAGES OF SWOT ANALYSIS
SWOT Analysis forms a thinking model for organizational managements as an approach and analysis technique. This model gives one the opportunity to limit the agenda in the steps of information gathering and interpretation, and shows the points that the decisions are based on. In other words, SWOT Analysis prepares the substructure for strategic decisions.
SWOT Analysis fits other theories and strategic decision tools. For example, SWOT encompasses a number of different forms of analysis, such as Porter’s Five Forces Model, Delphi Panel, Norton Balanced Score Card etc
. SWOT Analysis promotes group discussion about strategic issues and strategy development. By using creative participatory techniques such as brain storming, group meetings, it enables the pool knowledge.
SWOT Analysis helps organizational managements to start a discussion for the future and goals of the organization by moving beyond daily problems and the current situation.
SWOT Analysis can be applied at different analytical levels -individual level, organizational level, national level, international level-. It can be used by educational institutes, non-profit organizations, countries, governments, projects on multiculturalism etc.
6. DISADVANTAGES AND LIMITATIONS OF SWOT ANALYSIS
SWOT Analysis overemphasizes a single dimension of strategy. Sometimes organizations become preoccupied with a single strength or a key feature of the product or service they are offering and ignore other factors needed for competitive success.
SWOT Analysis is rarely deployed at lower than the organization level. This is a risky situation that each strength and weakness is related to and equally important for all strategic business units and the products organization produces. This can even lead to wrong strategies for the entire organization. Finally, SWOT Analysis very popular and useful in business management. It has much to offer, but only as a starting point. SWOT Analysis is a situation analysis and it can also be the starting point for a more comprehensive review. It is important because it can inform later steps in planning to achieve the organizational objectives. SWOT Analysis is a summary tool, often featured in business planning that can be applied and used beneficially in any decision-making process or to analyse a situation. Though it can be a valuable planning tool.
7. CONCLUSION




Comments
Post a Comment